上篇博文介绍过,Pytest是目前比较成熟功能齐全的测试框架,使用率肯定也不断攀升。
在实际工作中,许多测试用例都是类似的重复,一个个写最后代码会显得很冗余。这里,我们来了解一下@pytest.mark.parametrize装饰器,可以很好解决上述问题。
源代码分析
-
def parametrize(self,argnames, argvalues, indirect=False, ids=None, scope=None): -
""" Add new invocations to the underlying test function using the list -
of argvalues for the given argnames. Parametrization is performed -
during the collection phase. If you need to setup expensive resources -
see about setting indirect to do it rather at test setup time. # 使用给定argnames的argValue列表向基础测试函数添加新的调用,在收集阶段执行参数化。 -
:arg argnames: a comma-separated string denoting one or more argument -
names, or a list/tuple of argument strings. # 参数名:使用逗号分隔的字符串,列表或元祖,表示一个或多个参数名 -
:arg argvalues: The list of argvalues determines how often a -
test is invoked with different argument values. If only one -
argname was specified argvalues is a list of values. If N -
argnames were specified, argvalues must be a list of N-tuples, -
where each tuple-element specifies a value for its respective -
argname. # 参数值:只有一个argnames,argvalues则是值列表。有N个argnames时,每个元祖对应一组argnames,所有元祖组合成一个列表 -
:arg indirect: The list of argnames or boolean. A list of arguments' -
names (self,subset of argnames). If True the list contains all names from -
the argnames. Each argvalue corresponding to an argname in this list will -
be passed as request.param to its respective argname fixture -
function so that it can perform more expensive setups during the -
setup phase of a test rather than at collection time. -
:arg ids: list of string ids, or a callable. -
If strings, each is corresponding to the argvalues so that they are -
part of the test id. If None is given as id of specific test, the -
automatically generated id for that argument will be used. -
If callable, it should take one argument (self,a single argvalue) and return -
a string or return None. If None, the automatically generated id for that -
argument will be used. -
If no ids are provided they will be generated automatically from -
the argvalues. # ids:字符串列表,可以理解成标题,与用例个数保持一致 -
:arg scope: if specified it denotes the scope of the parameters. -
The scope is used for grouping tests by parameter instances. -
It will also override any fixture-function defined scope, allowing -
to set a dynamic scope using test context or configuration. -
# 如果指定,则表示参数的范围。作用域用于按参数实例对测试进行分组。 -
它还将覆盖任何fixture函数定义的范围,允许使用测试上下文或配置设置动态范围。 -
"""
argnames
释义:参数名称。
格式:字符串"arg1,arg2,arg3"。
aegvalues
释义:参数值列表。
格式:必须是列表,如[val1,val2,val3]。
-
单个参数,里面是值的列表,如@pytest.mark.parametrize("name",["Jack","Locus","Bill"]);
-
多个参数,需要用元祖来存放值,一个元祖对应一组参数的值,如@pytest.mark.parametrize("user,age",[("user1",15),("user2",24),("user3",25)])。
ids
释义:可以理解为用例的id。
格式:字符串列表,如["case1","case2","case3"]。
indirect
释义:当indirect=True时,若传入的argnames是fixture函数名,此时fixture函数名将成为一个可执行的函数,argvalues作为fixture的参数,执行fixture函数,最终结果再存入request.param。
当indirect=False时,fixture函数只作为一个参数名给测试收集阶段调用。
备注:这里可以将the setup phase(测试设置阶段)理解为配置 conftest.py 阶段,将the collection phase(测试收集阶段)理解为用例执行阶段。
装饰测试类
-
import pytest -
data = [ -
(2,2,4), -
(3,4,12) -
] -
def add(a,b): -
return a * b -
@pytest.mark.parametrize('a,b,expect',data) -
class TestParametrize(object): -
def test_parametrize_1(self,a,b,expect): -
print('\n测试函数1测试数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a,b)) -
assert add(a,b) == expect -
def test_parametrize_2(self,a,b,expect): -
print('\n测试函数2测试数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a,b)) -
assert add(a,b) == expect -
if __name__ == "__main__": -
pytest.main(["-s","test_07.py"])
-
============================= test session starts ============================= -
platform win32 -- Python 3.8.0, pytest-6.2.5, py-1.11.0, pluggy-1.0.0 -
rootdir: D:\AutoCode -
plugins: html-3.1.1, metadata-1.11.0 -
collecting ... collected 4 items -
test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_1[2-2-4] -
测试函数1测试数据为 -
2-2 -
PASSED -
test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_1[3-4-12] -
测试函数1测试数据为 -
3-4 -
PASSED -
test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_2[2-2-4] -
测试函数2测试数据为 -
2-2 -
PASSED -
test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_2[3-4-12] -
测试函数2测试数据为 -
3-4 -
PASSED -
============================== 4 passed in 0.12s ============================== -
Process finished with exit code 0
由以上代码可以看到,当装饰器装饰测试类时,定义的数据集合会被传递给类的所有方法。
装饰测试函数
单个数据
-
import pytest -
data = ["Rose","white"] -
@pytest.mark.parametrize("name",data) -
def test_parametrize(name): -
print('\n列表中的名字为\n{}'.format(name)) -
if __name__ == "__main__": -
pytest.main(["-s","test_07.py"])
-
============================= test session starts ============================= -
platform win32 -- Python 3.8.0, pytest-6.2.5, py-1.11.0, pluggy-1.0.0 -
rootdir: D:\AutoCode -
plugins: html-3.1.1, metadata-1.11.0 -
collected 2 items -
test_07.py -
列表中的名字为 -
Rose -
. -
列表中的名字为 -
white -
. -
============================== 2 passed in 0.09s ============================== -
Process finished with exit code 0
当测试用例只需要一个参数时,我们存放数据的列表无序嵌套序列,@pytest.mark.parametrize("name", data) 装饰器的第一个参数也只需要一个变量接收列表中的每个元素,第二个参数传递存储数据的列表,那么测试用例需要使用同名的字符串接收测试数据(实例中的name)且列表有多少个元素就会生成并执行多少个测试用例。
一组数据
-
import pytest -
data = [ -
[1, 2, 3], -
[4, 5, 9] -
] # 列表嵌套列表 -
# data_tuple = [ -
# (1, 2, 3), -
# (4, 5, 9) -
# ] # 列表嵌套元组 -
@pytest.mark.parametrize('a, b, expect', data) -
def test_parametrize_1(a, b, expect): # 一个参数接收一个数据 -
print('\n测试数据为\n{},{},{}'.format(a, b, expect)) -
actual = a + b -
assert actual == expect -
@pytest.mark.parametrize('value', data) -
def test_parametrize_2(value): # 一个参数接收一组数据 -
print('\n测试数据为\n{}'.format(value)) -
actual = value[0] + value[1] -
assert actual == value[2] -
if __name__ == "__main__": -
pytest.main(["-s","test_07.py"])
-
============================= test session starts ============================= -
platform win32 -- Python 3.8.0, pytest-6.2.5, py-1.11.0, pluggy-1.0.0 -
rootdir: D:\AutoCode -
plugins: html-3.1.1, metadata-1.11.0 -
collected 4 items -
test_07.py -
测试数据为 -
1,2,3 -
. -
测试数据为 -
4,5,9 -
. -
测试数据为 -
[1, 2, 3] -
. -
测试数据为 -
[4, 5, 9] -
. -
============================== 4 passed in 0.09s ============================== -
Process finished with exit code 0
当测试用例需要多个数据时,我们可以使用嵌套序列(嵌套元组&嵌套列表)的列表来存放测试数据。
装饰器@pytest.mark.parametrize()可以使用单个变量接收数据,也可以使用多个变量接收,同样,测试用例函数也需要与其保持一致。
当使用单个变量接收时,测试数据传递到测试函数内部时为列表中的每一个元素或者小列表,需要使用索引的方式取得每个数据。当使用多个变量接收数据时,那么每个变量分别接收小列表或元组中的每个元素列表嵌套多少个多组小列表或元组,测生成多少条测试用例。
组合数据
-
import pytest -
data_1 = [1,2,3] -
data_2 = ['a','b'] -
@pytest.mark.parametrize('a',data_1) -
@pytest.mark.parametrize('b',data_2) -
def test_parametrize_1(a,b): -
print(f'笛卡尔积测试结果为:{a},{b}') -
if __name__ == '__main__': -
pytest.main(["-vs","test_06.py"])

通过测试结果,我们不难分析,一个测试函数还可以同时被多个参数化装饰器装饰,那么多个装饰器中的数据会进行交叉组合的方式传递给测试函数,进而生成n * n个测试用例。
标记用例
-
import pytest -
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[ -
("3+5",8), -
("2+4",6), -
pytest.param("6 * 9",42,marks=pytest.mark.xfail), -
pytest.param("6 * 6",42,marks=pytest.mark.skip) -
]) -
def test_mark(test_input,expected): -
assert eval(test_input) == expected -
if __name__ == '__main__': -
pytest.main(["-vs","test_06.py"])
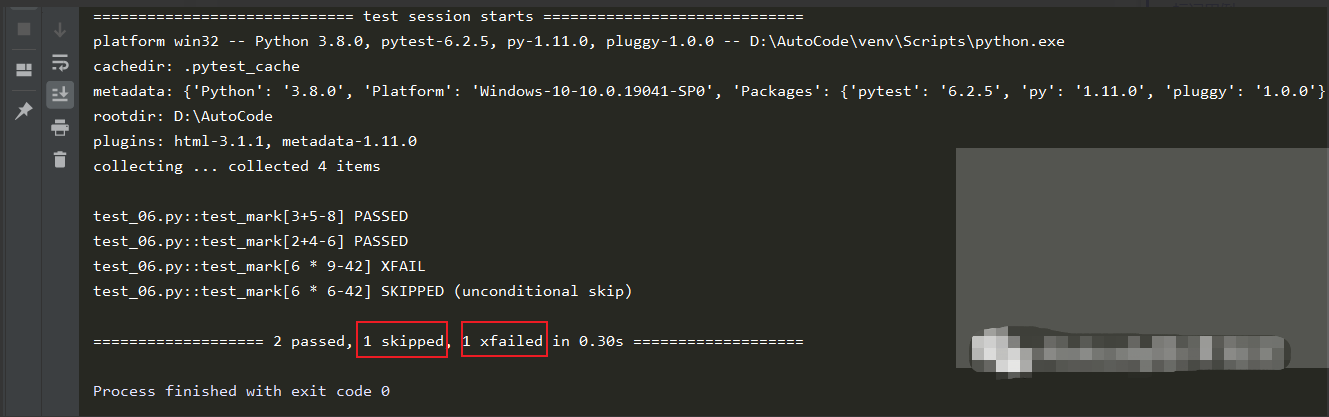
输出结果显示收集到4个用例,两个通过,一个被跳过,一个标记失败:
-
当我们不想执行某组测试数据时,我们可以标记skip或skipif;
-
当我们预期某组数据会执行失败时,我们可以标记为xfail等。
嵌套字典
-
import pytest -
data = ( -
{ -
'user': "name1", -
'pwd': 123 -
}, -
{ -
'user': "name2", -
'pwd': 456 -
} -
) -
@pytest.mark.parametrize('dic',data) -
def test_parametrize(dic): -
print('\n测试数据为\n{}'.format(dic)) -
if __name__ == '__main__': -
pytest.main(["-vs","test_06.py"])
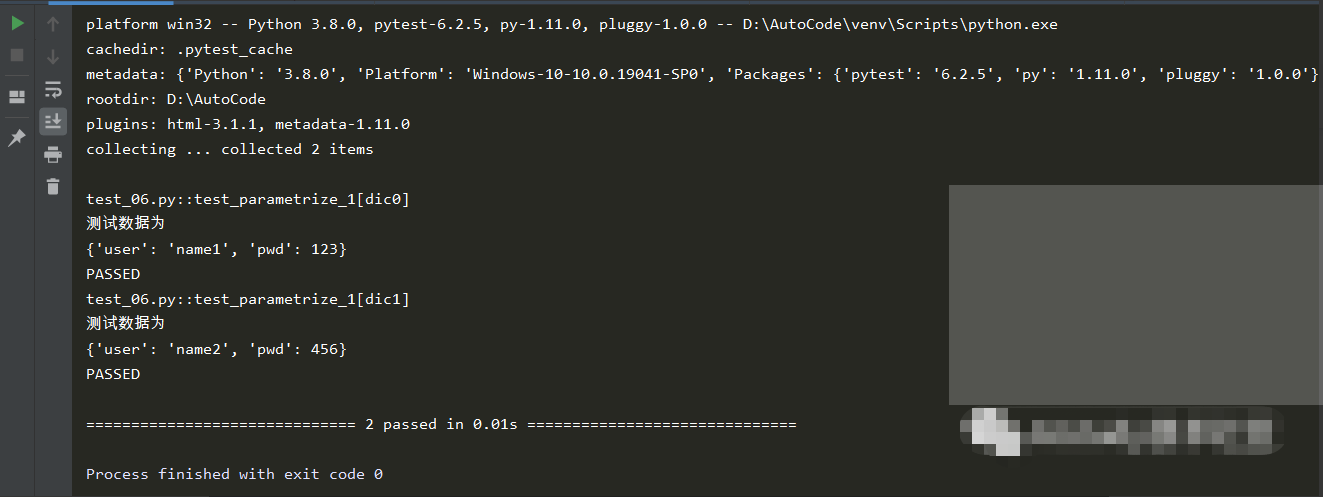
增加测试结果可读性
参数化装饰器有一个额外的参数ids,可以标识每一个测试用例,自定义测试数据结果的显示,为了增加可读性,我们可以标记每一个测试用例使用的测试数据是什么,适当的增加一些说明。
在使用前你需要知道,ids参数应该是一个字符串列表,必须和数据对象列表的长度保持一致。
-
import pytest -
data_1 = [ -
(1, 2, 3), -
(4, 5, 9) -
] -
ids = ["a:{} + b:{} = expect:{}".format(a, b, expect) for a, b, expect in data_1] -
def add(a, b): -
return a + b -
@pytest.mark.parametrize('a, b, expect', data_1, ids=ids) -
class TestParametrize(object): -
def test_parametrize_1(self, a, b, expect): -
print('\n测试函数1测试数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a, b)) -
assert add(a, b) == expect -
def test_parametrize_2(self, a, b, expect): -
print('\n测试函数2数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a, b)) -
assert add(a, b) == expect -
if __name__ == '__main__': -
pytest.main(["-v","test_06.py"])
-
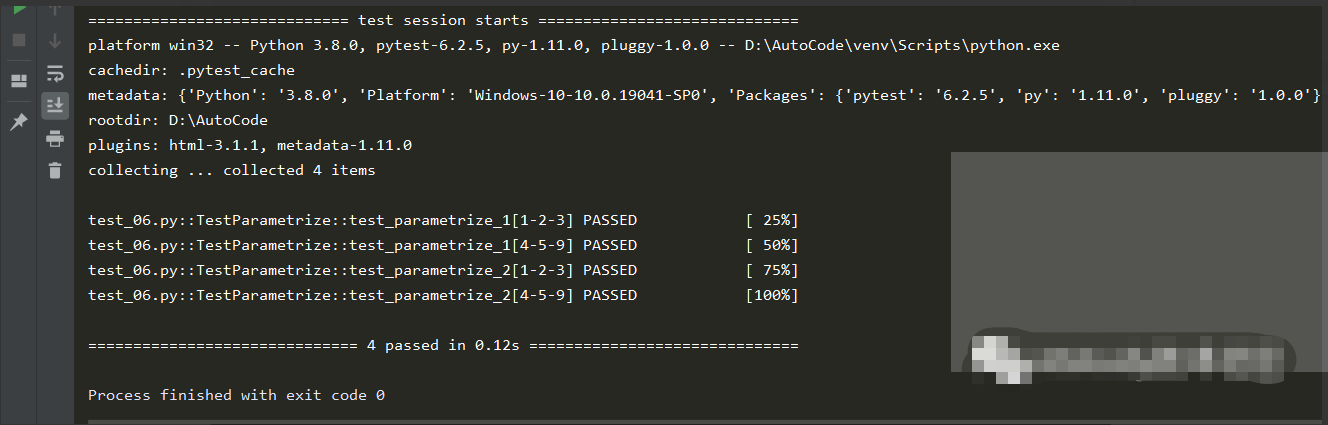
不加ids参数的返回结果:
-
加ids参数的返回结果:
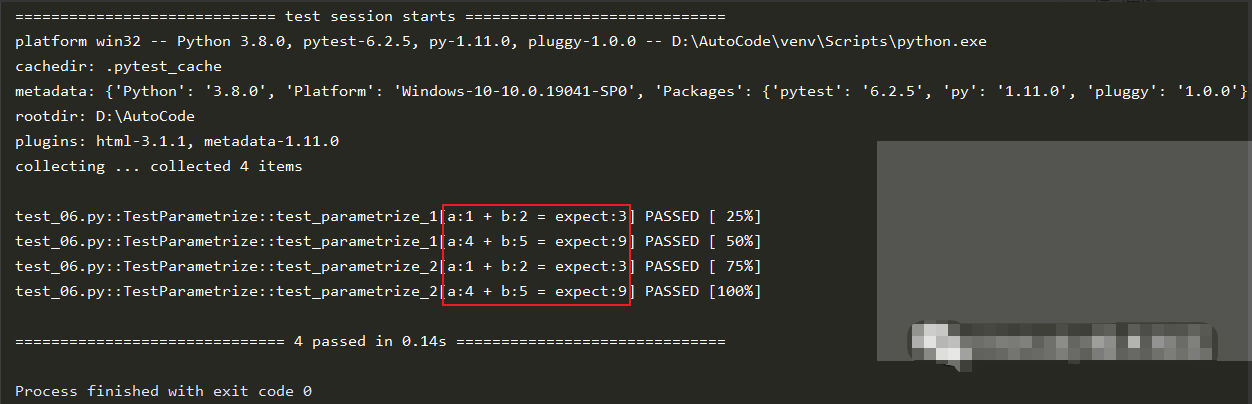
我们可以看到带ids参数的返回结果中的用例都被一个列表明确的标记了,而且通过这种标记可以更加直观的看出来,每个测试用例使用的数据名称及测试内容。
行动吧,在路上总比一直观望的要好,未来的你肯定会感 谢现在拼搏的自己!如果想学习提升找不到资料,没人答疑解惑时,请及时加入扣群: 320231853,里面有各种软件测试+开发资料和技术可以一起交流学习哦。
最后感谢每一个认真阅读我文章的人,礼尚往来总是要有的,虽然不是什么很值钱的东西,如果你用得到的话可以直接拿走:

这些资料,对于【软件测试】的朋友来说应该是最全面最完整的备战仓库,这个仓库也陪伴上万个测试工程师们走过最艰难的路程,希望也能帮助到你!